
AI integration with CRM and ERP: do’s and don’ts
Dec 21, 2025
AI only creates real value once it lives inside your core systems. For SMBs in wholesale, distribution, manufacturing, installation, accounting, and professional services, that means smart, secure AI integration with CRM and ERP. This article gives you a practical guide with do’s and don’ts, a workable blueprint, and a 90-day plan to move from pilot to scalable impact.
Why integrate AI with CRM and ERP?
CRM contains context about accounts, deals, and communication. ERP contains prices, inventory, orders, contracts, and invoices. AI without access to that reality often produces generic or incorrect output.
With integration, you can speed up quoting, automatically triage customer questions, factor inventory and lead likelihood into prioritization, and reduce repetitive admin work with an audit trail in your source systems.
Teams feel it immediately: less manual work, faster cycle times, and better data quality in CRM and ERP.
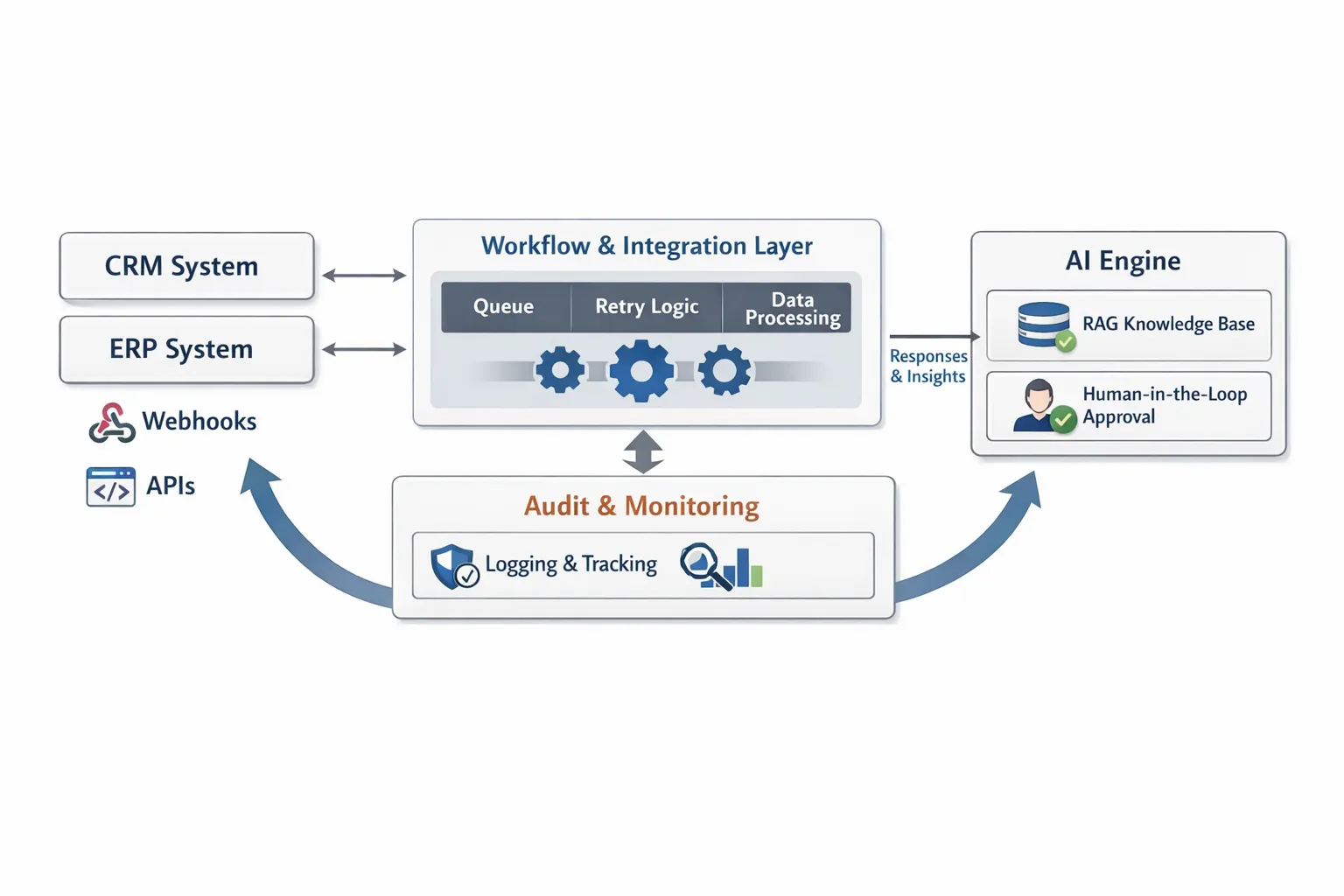
Architecture at a glance
Most SMB implementations work best with a lightweight, modular setup: triggers from CRM or ERP, a workflow layer that orchestrates AI, retrieval of company knowledge, a human-in-the-loop step for higher-risk actions, and safe write-back synchronization.
The do’s: what works in practice
Start with one clearly scoped use case with a KPI and baseline. Think time-to-quote, first response time, number of manual CRM updates per day, or quote accuracy.
Keep CRM and ERP as the source of truth. Let AI make suggestions, generate enrichments, and execute tasks, but write back with a clear audit trail to the right objects and fields.
Use RAG for factual knowledge. Retrieve up-to-date product info, prices, inventory, contract terms, and policies from ERP, PIM, or a knowledge base instead of letting the model hallucinate.
Build secure integrations. Use service accounts, scoped API keys, secret vaults, IP allowlists, encryption in transit and at rest, and strict separation between test and production.
Make actions idempotent. Use unique correlation IDs, deduplication, and idempotent endpoints so timeouts or retries do not create duplicate orders, notes, or tasks.
Control latency with a budget per step. Define what must be real time versus what can be asynchronous. For example, agent-assist in CRM should stay under 2 seconds, overnight enrichment can take longer.
Use human-in-the-loop for higher-risk tasks. Have employees approve AI-generated quotes, discounts outside policy, or contract text inside CRM or ERP workflows.
Version prompts and evaluations. Treat prompts like code, track versions, test with representative datasets, and measure quality after each model update.
Monitor models and business KPIs. Track precision and recall for classification, intent accuracy for triage, output accuracy for quotes, plus operational metrics like latency and error rates.
Log everything that matters. Store input-output, model version, prompt version, decision rationale, and who or what approved it. This is essential for quality assurance and compliance.
Respect GDPR and the EU AI Act. Minimize data, pseudonymize where possible, document risk assessment and intended use, and maintain your technical file and policies.
Plan for maintenance. AI and APIs change, so schedule regression tests, retraining or knowledge updates, and lifecycle management for integrations.
The don’ts: common mistakes to avoid
Never let AI manage your master data. AI can suggest changes or trigger workflows, but master data and transactions should be validated and recorded in CRM and ERP.
Do not connect directly to production without a staged rollout. Start read-only, use a sandbox, then enable limited write scopes, and activate gradually per team or region.
Do not write free text into critical fields. Keep a clear split between structured fields and AI-generated explanations so reporting remains correct.
Do not rely on prompt magic. Without an evaluation set, acceptance criteria, and regression tests, quality becomes random and hard to reproduce.
Do not ignore identities and keys. Use external IDs, mapping, and dedup logic, otherwise you get duplicate accounts, mismatches, or wrong links.
Never store secrets in scripts or no-code fields. Use a secrets manager, rotate keys, and limit privileges to the minimum necessary scopes.
Do not over-automate customer signals. Never run outbound AI email or pricing proposals fully autonomously outside policy and without throttling.
Do not assume one vendor solves everything. Use an adapter pattern so you can swap your AI engine or CRM without rewriting the whole integration.
Do not forget edge cases. Multilingual support, VAT rules, currencies, tiered discounts, backorders, and delivery exceptions require explicit logic and tests.
Do not treat integration as a one-off project. Without maintenance, monitoring, and clear ownership, your solution ages and quality drops.
Strong use cases by industry
Wholesale and distribution: a smart quoting copilot that checks price and inventory, flags discount-policy deviations, and creates a task or proposal in CRM. Automatic order status updates from ERP to CRM and email, including cross-sell suggestions based on purchase history.
B2B product suppliers: AI-driven lead scoring in CRM enriched with ERP order history, prioritization by revenue potential and lead time. Automatic generation of product specs and datasheets in quotes based on RAG.
Accounting and boutique legal firms: intake triage and case summaries into CRM, time-entry suggestions from email and calendar, first draft for engagement letters with human-in-the-loop.
Local manufacturing and installation: service ticket triage linked to ERP parts and work orders, automatic job report summaries in CRM after a site visit, proactive maintenance suggestions based on sensor data and historical records.
B2B real estate: AI extraction of property attributes from PDFs into CRM, lead qualification based on criteria and budget, automatic appointment scheduling and pipeline updates with an audit trail.
Chatbots and support integrated with CRM and ERP
For product support and aftersales, a chatbot connected to your CRM and ERP works especially well. You can quickly give customers order status and delivery times, personalize knowledge base articles, and triage cases to the right queue. Strong practice examples show that internal AI chatbots can significantly reduce response times. See this explanation of how an internal chatbot speeds up support teams and delivers more consistent answers, including implementation steps, in the article on AI chatbots transforming product support.
90-day implementation plan
Diagnosis and design: identify 1 high-friction process, define clear KPIs and measure a baseline, map data flows, permissions, and field mapping, choose the integration pattern, and define the human-in-the-loop step.
Build and validate the pilot: start read-only, implement RAG with a limited knowledge source, version prompts and set up an evaluation set, integrate with sandbox CRM and ERP, enable logging and monitoring, train a small team, and run in parallel for 2 weeks.
Scale in phases: enable write-backs with limited scopes, expand the knowledge source and triggers, set alerts and throttling, document the technical file and working agreements, roll out per team or region, and review KPIs weekly.
KPIs that matter
Cycle time: time-to-quote or first response time in support and sales.
Quality: quote accuracy, classification precision and recall, first contact resolution (FCR) in support.
Productivity: number of manual CRM updates removed, tasks automatically completed, time per case or order.
Revenue and margin: higher conversion per stage, better upsell and cross-sell performance, fewer discounts outside policy.
Data quality: field completeness, duplicates, consistency between CRM and ERP.
Risk and compliance: number of exceptions that hit human-in-the-loop, audit completeness, incident rate.
Governance, security, and compliance in plain English
Data minimization: send only the fields AI truly needs, pseudonymize where possible, and set retention periods.
Authorization and roles: limit what AI can read and write, log who or what changed something, with what rationale and version.
EU AI Act and policy: document purpose, risks, controls, evaluations, and fallback. Ensure users understand what AI does, when a human reviews, and how they can intervene.
Incident response: define what happens with incorrect write-backs, latency spikes, or model drift, including rollback and a communication plan.
Choices in integration and technology
Interfaces: prefer official APIs and webhooks from your CRM and ERP. An iPaaS or a lightweight workflow engine helps with retries, scheduling, mapping, and monitoring.
AI capability: start pragmatically with generative tasks plus retrieval. Fine-tuning can help for fixed formats and sufficient proprietary data, but it is not required to get results.
Observability: include tracing, metrics, and structured logging from day one so you can quickly find root causes when errors or quality issues occur.
Build, buy, or partner
Buy: if your use case is standard, like email triage, summarization, or basic lead scoring. You save time, as long as integrations and data policy fit.
Build: if your process, data, and compliance requirements are unique, and customization is your competitive advantage. Expect ongoing maintenance, evaluation, and security work.
Partner: if you want to deliver fast but still be confident in good choices, secure integration, and continuous optimization. B2B GrowthMachine helps SMB teams with AI-driven sales and operations automation, CRM and ERP integrations, and continuous monitoring and improvement.
Summary and next step
Small, well-scoped integrations deliver the fastest value. Connect AI to your CRM and ERP with clear KPIs, safe write-backs, RAG for factual accuracy, and human-in-the-loop for higher-risk steps. Measure, improve, and scale in phases. That is how you build a robust AI growth engine that takes weeks, not months, to create impact.
If you want to deliver this within 90 days while maintaining control and compliance, schedule a strategy call. B2B GrowthMachine delivers AI-driven sales and operations automation, an assistant for daily tasks, seamless system integrations with CRM and ERP, and continuous optimization so your team works faster, smarter, and at lower cost.