
Customer Support Chatbot: Setup Checklist for SMEs
Jan 14, 2026
Most SMEs don’t need “a chatbot.” They need a reliable, measurable support system that:
answers repetitive questions accurately
collects the missing details up front
routes complex cases to the right person
triggers real actions in CRM, ERP, or ticketing
This checklist is built for B2B SMEs (wholesale, distribution, professional services, installation, and B2B real estate) where questions are often account-specific, time-sensitive, and tied to operational systems.
1) Define the chatbot’s job (and what it must not do)
Before you touch tools or prompts, decide what “success” looks like operationally.
Setup checklist
Primary goal: Pick one primary outcome (reduce inbound tickets, speed up order status answers, increase first-contact resolution, shorten time-to-quote).
Scope boundaries: Write down what the bot is allowed to handle and what it must always escalate (pricing exceptions, contract terms, complaints, cancellations).
Risk tiering: Mark intents as low-risk (FAQ), medium-risk (account-specific but read-only), high-risk (anything that changes orders, financial data, or legal commitments).
Definition of done: Agree on 3–5 launch KPIs and minimum acceptable thresholds (for example, a maximum “I don’t know” rate for top questions).
If you want a deeper B2B view on what works beyond FAQ bots, use this as a companion read: customer service chatbot AI patterns that work in B2B.
2) Choose channels and entry points (where the bot should live)
In B2B, “customer support” is often spread across email, phone, WhatsApp, portals, and sales inboxes. A website widget alone rarely moves the needle.
Setup checklist
Channel priority: Select 1–2 channels for phase 1 (website chat plus WhatsApp, or email triage plus portal).
Entry points: Decide where the bot appears (help center, pricing/quote page, logged-in portal, order tracking page, invoice page).
Identity strategy: Decide if the bot is anonymous (public FAQ) or authenticated (account-aware answers).
Human availability: Align chatbot promises with real staffing, otherwise you will create frustration (for example, do not offer “live handoff” if nobody can accept it).
3) Inventory your top questions (and classify them by intent)
A customer support chatbot is only as good as the problem selection. Start with volume and business impact.
Setup checklist
Top 25–50 questions: Pull from tickets, email subject lines, call reasons, and chat logs.
Intent buckets: Categorize each question (order status, delivery ETA, returns, invoice copy, product availability, technical specs, installation planning, contract and SLA).
Required inputs: List what the bot must collect for each intent (order number, account name, site address, serial number, preferred delivery date).
Best answer source: Decide whether the answer should come from a knowledge base, CRM, ERP, or a human.
A fast win for many SMEs is improving intake quality and routing, even before you automate “perfect answers.”
4) Prepare the knowledge base (so answers are grounded, not guessed)
For modern AI chatbots, the key question is not “how smart is the model?” It’s “can it retrieve the right internal truth, consistently?” Many teams use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to ground answers in approved sources.
Setup checklist
Single source of truth: Choose where approved content lives (help center, internal wiki, product sheets, policy PDFs).
Content cleanup: Remove outdated pricing, old terms, and duplicate pages (duplicates increase inconsistent answers).
Answer style guide: Define tone, disclaimers, and what must be included (for example, lead times depend on stock, include cut-off times).
Citation behavior: Decide whether the bot should reference sources (recommended for internal agent assist, optional for public chat).
Knowledge refresh process: Assign an owner and a weekly or biweekly update cadence.
If you are designing service as a measurable system (not just a widget), this pairs well with: customer service with AI, faster responses, higher NPS.
5) Plan integrations (what the bot must read and what it can write)
In B2B support, the highest ROI often comes from connecting the chatbot to operational systems.
A practical rule: start with read access first, then introduce guarded writes only when quality is proven.
Setup checklist
Ticketing integration: Create tickets with structured fields (intent, urgency, customer type, required identifiers).
CRM integration: Lookup account, contract tier, SLA, and contact details.
ERP or order system integration: Read order status, delivery ETA, backorders, invoices (often the biggest deflection win for wholesalers and suppliers).
Access controls: Ensure the bot only exposes what the user is authorized to see.
Write actions policy: Define which actions are allowed (create ticket, schedule callback, generate RMA request) and which require approval.
For integration guardrails, see: AI integration with CRM and ERP, do’s and don’ts.
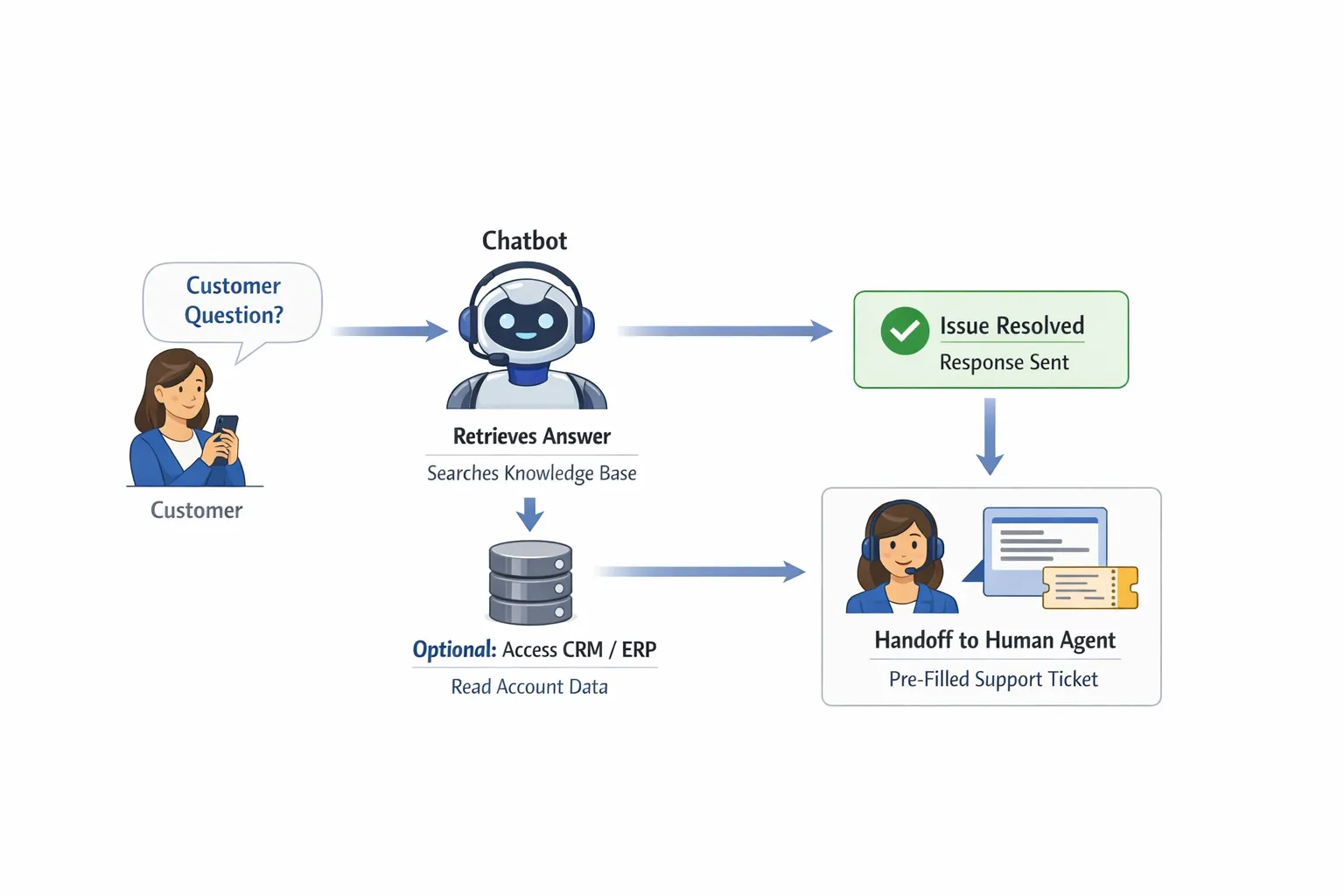
6) Design the conversation (short, structured, and bias-resistant)
Great support chats feel natural, but they are usually built on structured conversation patterns.
Setup checklist
Happy path scripts: Write the ideal flow for each top intent (what the bot asks first, what it checks, what it responds).
Structured intake: Use forms or guided questions where accuracy matters (order number, location, product SKU).
Fallback behavior: Define what happens when confidence is low (ask one clarifying question, then escalate).
No hallucination rule: Instruct the bot to say “I don’t have that information” rather than inventing.
Confirmation step: Before any action, show a summary and ask the user to confirm.
7) Build human handoff that actually helps your team
If the chatbot escalates without context, it increases workload. The handoff should reduce agent effort, not add a new channel to monitor.
Setup checklist
Handoff triggers: Define escalation rules (negative sentiment, payment dispute, repeated fallback, high-risk intents).
Routing logic: Route by topic, customer tier, geography, or product line.
Context package: Include the transcript, collected fields, account details, and what the bot already tried.
SLA alignment: If you promise response times, align staffing and on-call coverage.
Agent assist option: Consider an internal assist mode that drafts responses while a human sends the final reply.
8) Privacy, security, and compliance (minimum viable controls)
Even SMEs should treat support chat as a production system, especially when it touches customer data.
Depending on your region and customers, you may need to account for frameworks and regulation such as the GDPR and the EU AI Act. For risk guidance, the NIST AI Risk Management Framework is also a useful baseline for governance conversations.
Setup checklist
Data minimization: Collect only what you need (avoid requesting full invoices, IDs, or sensitive details in chat).
PII rules: Define what counts as personal data in your context and how it is handled.
Retention policy: Decide how long transcripts are stored and where.
Vendor review: Verify data processing terms, sub-processors, and security posture.
Audit trail: Log key actions (ticket created, status pulled, refund request initiated) with timestamps and identifiers.
9) QA and testing (before you put it in front of customers)
Most chatbot failures are predictable, and preventable, if you test with real questions and edge cases.
Setup checklist
Golden set: Create a test set of 50–200 real customer questions (including messy phrasing and incomplete details).
Red team prompts: Test jailbreak attempts, data extraction requests, and “make something up” prompts.
Grounding checks: Verify that answers match your approved sources.
Integration safety: Test rate limits, timeouts, and safe failure modes (what happens when ERP is down).
Brand and legal review: Validate disclaimers and escalation language.
If you want a production mindset for AI quality controls, this is highly relevant: AI checks for production monitoring that prevents errors.
10) Define your KPIs (and instrument them from day one)
If you cannot measure it, you cannot improve it. Avoid vanity metrics like “number of chats.” Track outcomes that tie to cost-to-serve and customer experience.
Setup checklist
Containment rate: Percent resolved without human involvement.
First response time: Time to first meaningful answer.
First contact resolution: Percent solved in a single interaction.
Escalation quality: Percent of escalations that include all required fields.
Fallback rate: Percent of chats where the bot fails to answer.
Time to quote (if relevant): For support-to-sales questions.
If your broader goal is measurable CX improvement, you may also like: AI to improve customer experience with measurable improvements.
11) Launch in phases (avoid “big bang” rollouts)
A phased launch protects customers and lets you improve quickly.
Setup checklist
Phase 1 (shadow mode): Bot drafts answers for agents, agents send final replies.
Phase 2 (limited audience): Enable for a subset of customers, regions, or intents.
Phase 3 (broader rollout): Expand coverage once thresholds are met.
Rollback plan: If quality drops, you need an easy switch to revert to human-only.
Owner and cadence: Assign a weekly improvement review with clear responsibility.
12) Industry-specific “must cover” items for B2B SMEs
Use these to sanity-check your scope if you’re in one of the common SME segments we see.
Wholesale businesses, distributors, B2B product suppliers
Order status and delivery ETA (with cut-off times)
Backorders, substitutions, partial shipments
Invoice copy requests and payment status
Returns (RMA initiation) and warranty policy routing
Stock availability and lead times (with clear uncertainty handling)
Accountancy and legal boutiques
Secure intake (what documents are needed, how to upload safely)
Engagement scope clarification (what is included, what is out of scope)
Status updates on ongoing cases, with authentication
Appointment scheduling and deadline reminders
Installation companies selling to businesses
Job scheduling changes and site access requirements
Troubleshooting triage (collect model, serial number, photos)
Warranty and service contract checks
Parts availability and expected arrival
B2B real estate brokers
Lead qualification intake (use case, budget range, timeline)
Property availability updates and viewing scheduling
Document requests (NDAs, financial info) with secure handoff
Fast escalation to a human for negotiation and exceptions
When to use a plug-and-play chatbot vs. a custom AI workflow
A plug-and-play chatbot can be enough if your main need is FAQ deflection and basic ticket creation.
You should consider a more tailored approach when:
answers depend on account data (contracts, SLAs, pricing tiers)
your team loses time on order and invoice status questions
you want the bot to trigger actions (create tickets, request RMAs, update CRM)
you need reliability and monitoring because the process is business-critical
B2B GrowthMachine helps SMEs implement AI support systems that connect prompting, workflows, and agents to the tools you already use (CRM, ERP, email, WhatsApp, Slack, and APIs), with continuous optimization.
If you want help turning this checklist into a working rollout plan, start here: B2B GrowthMachine.